
What is a VPN, and Why Should You Care?
These days, in the modern world, privacy and security online are becoming more critical. Everything can be traced or disclosed, from personal data to surfing on the web. That is when VPNs come into play, which rapidly has become essential for anyone looking to keep their activity truly private online. But what is a VPN, and why should you be using one? The article that follows breaks down all you should know about VPNs, using tangible data from the real world and a case study to prove their importance.
Online Privacy Risks
Imagine you’re browsing the internet at a coffee shop or airport. You’re on a public Wi-Fi network, and while you’re sipping your coffee or waiting for your flight, your personal data is at risk. Public Wi-Fi networks are notoriously insecure, and hackers often lurk in the shadows, waiting to intercept your data. This is where a VPN comes into play.

Why Privacy Matters
Your online activities, from emails to online purchases, can be tracked and monitored. Without protection, your personal information, login credentials, and financial data are exposed to anyone with malicious intent. Moreover, your ISP (Internet Service Provider) can see and log all your online activities, which could lead to targeted advertisements or worse, data breaches.
Understanding VPNs
VPN- Virtual Private Network. The tool was created to enhance your online privacy and security. Here’s how it works:
Virtual
A VPN creates a “virtual” tunnel between your device and a VPN server. That means there is no physical cable to connect you directly to the VPN server but rather an assuring digital pathway that keeps your data encrypted.
Private
The VPN encrypts your internet traffic, also concealing your IP address. Whomever might try snooping around will find themselves staring at scrambled data with no meaningful information about either your location or your identity.
Network
It connects various devices, for instance, your computer and VPN server, into a network that is private and secure.
Real-World Impact: Case Study
Now, let’s take the example of a journalist in some country that highly censors the internet. In 2023, many journalists were heavily restricted by firewalls and surveillance imposed by a government from accessing and disseminating information. Such censorship will be bypassed by the use of a VPN for these journalists to access blocked websites and securely contact sources for stories. The practical scenario essentially illustrates the importance of a VPN in securing personal or professional online activities.
Advantages of Using a VPN
Why should you use a VPN? Here are a few of the key benefits:
Enhanced Security
A VPN encrypts all the information you send and receive over the internet. In this case, your information, such as your login details or credit card numbers, is protected from hackers. For example, many cybercriminals hack into public Wi-Fi networks. Having a VPN can help in ensuring that even should the hackers get their hands on your data, it would be encrypted and thus unreadable.
Less Online Tracking
The time you spend online without a VPN means any activity you perform, like visiting websites or staying on them, can be tracked by your ISP. The VPN masks your IP address, and thus, making it harder for an ISP and advertisers to track.
Access to Restricted Content
Many streaming services and websites block content based on your geographic location. With a VPN, you can connect with servers in other countries to access content not available in your region. As an example, you can watch a Netflix show available in the US even if you are residing in another country.
Safety with Public Wi-Fi
The majority of public Wi-Fi do not have security features; hence, they are easily targeted for any form of cyber attack. A VPN encrypts your connection to the Internet, adding additional hurdles that hackers must face in intercepting your data on public Wi-Fi.
Protection for Remote Workers
Organizations typically use a VPN to securely connect employees to the network from a remote location. This is quite significant in relation to sensitive business communications and data.
Common Misconceptions about VPNs
Despite their advantages, VPNs are often misunderstood. Here are some common misconceptions:
VPNs Make You Completely Anonymous
While a VPN changes your IP address, it doesn’t make you completely anonymous. Websites can still track the things you do with cookies or other tracking methods. But putting them together with a VPN and browser extensions focused on privacy does a better job.
VPNs Are Illegal
The use of a VPN is perfectly legal in most countries. Some countries limit or prohibit using VPNs. Always check local laws before using a VPN.
Free VPNs are just as good as paid ones.
Free VPNs are, many a time, accompanied by limitations such as speed, fewer servers to choose from, and other potential issues with privacy. They might also make money by advertising or collecting and selling your data. Generally speaking, paid-for VPNs do better and offer more secure levels of privacy.
How VPNs Work: A Step-by-Step Guide
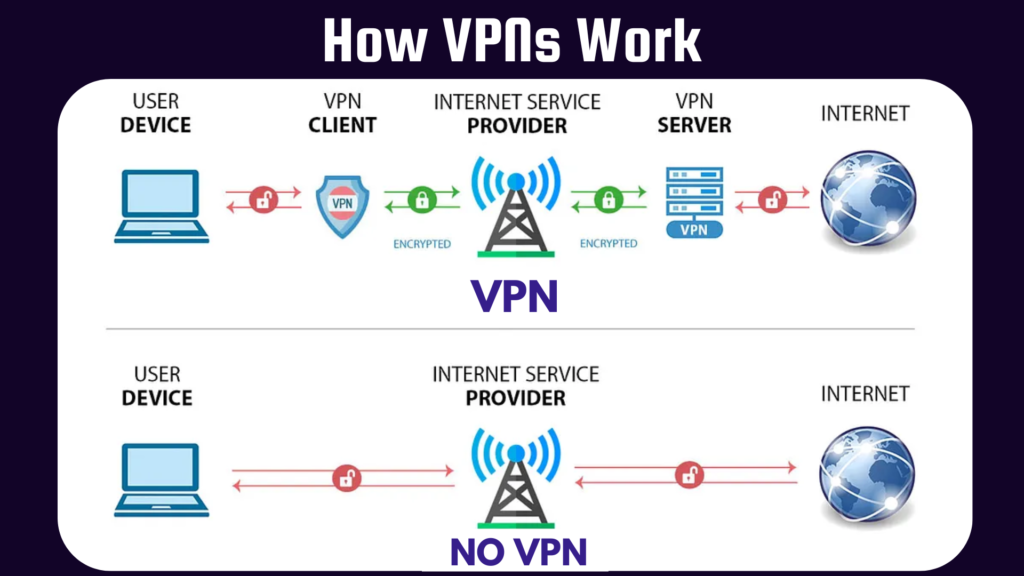
Understanding how a VPN works will help explain its function:
Authentication: When you connect to a VPN, the service authenticates your credentials, thereby ensuring you are authorized to access the network.
Data is encrypted before being sent over the Internet. It is scrambled with this encryption, making the data unreadable to someone intercepting it.
Encapsulation: After encryption, the data is then encapsulated within data packets. This adds another level of security because it makes the data packets more difficult to identify.
Tunneling: Data packets will be moved securely inside a tunnel all the way to the server. In that manner, the data is secured against interception.
Decryption: Once the data reaches the VPN server, it is decrypted and forwarded to its final destination. The return data undergoes the same process in reverse before it reaches you.
Types of VPNs
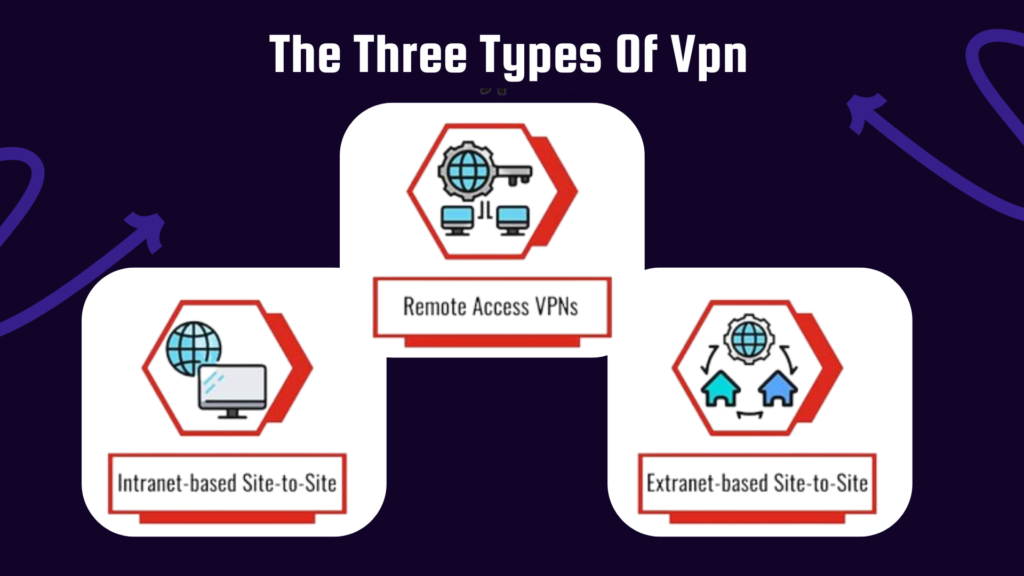
There is more than one kind of VPN that suits different needs.
- Site-to-Site VPN
These are used by organizations in order to connect several office locations securely. While site-to-site VPNs are complex to establish, they provide robust connectivity for large networks.
- Remote Access VPN
This type allows individual users to connect to a network remotely, such as employees accessing their company’s network from home.
- Personal VPNs
Personal VPNs are designed for individual users, can be easily set up and used, and thus provide privacy and security for personal use of the internet.
Choosing the Right VPN
Selecting the right VPN depends on several factors:
1. Speed: Look for a VPN with fast speeds and unlimited bandwidth to avoid slow connections.
2. Security: The VPN must use strong encryption standards, like AES-256.
3. Price: Free VPNs often have limitations and privacy concerns. A premium VPN usually offers better features and performance.
4. Reputation: Read user reviews and expert ratings about the VPN concerning reliability and performance.
5. Servers and Locations: A VPN with an extended range of servers and more locations promises to be much faster, hence accessing lots of content.
6. Privacy: Go for a VPN that respects privacy, does not log, and sells your data.
Also Read: Discover the Truth About Pakistan’s Internet Issues
Conclusion In a time when online security and privacy have become huge concerns, information on understanding and utilizing a VPN will help more than ever. The virtual private network adds that extra layer of protection through encryption of data, IP address masking, and the ability to bypass geographic restrictions. With the right choice of VPN, you can keep yourself safe from any kind of breach online, irrespective of your geographical location in the world. Whether browsing from a public Wi-Fi network, accessing restricted content, or simply caring about protecting your personal data, a VPN is just that mighty tool that will make a huge difference in your online experience.
